Italy speeds up its economic recovery, raising hopes for a new “Renaissance”. 2021 will be a year of growth for companies. Digitisation, sustainability, and training will lead the industry towards the fourth industrial revolution
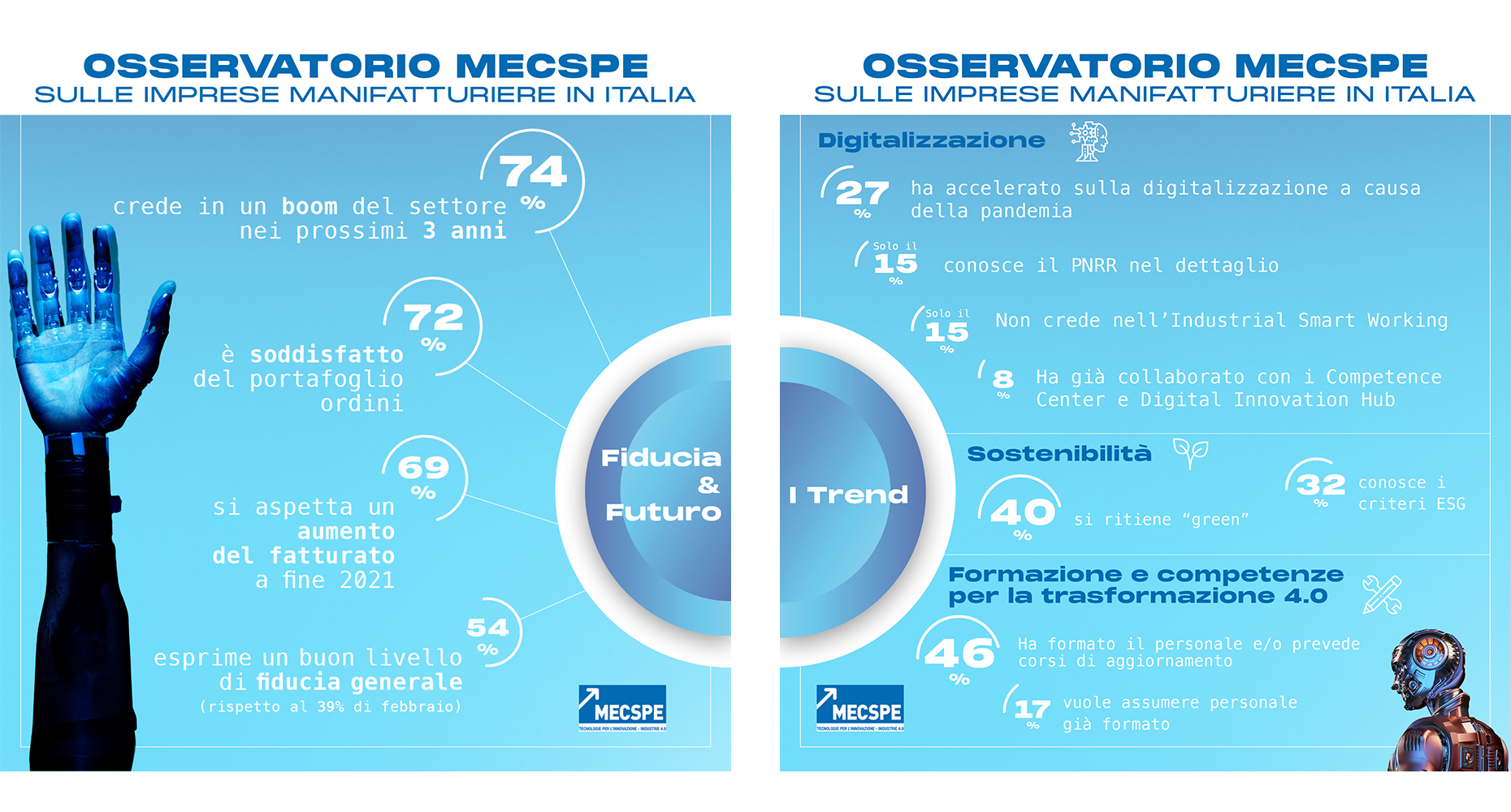
- Manufacturing companies feel confident (74% believe that the sector’ will boom again within the next 3 years) and happy with their order portfolio (72% think it’s adequate). Turnover forecasts are reassuring (69% believe that 2021 will end with positive results)
- There’s no growth without digitisation. Italy’s National Recovery and Resilience Plan (NRRP) will be crucial for the sector, although only 15% of entrepreneurs know it in detail. Many companies are happy with Industrial Smart Working.
- Going green is the only option. 4 companies out of 10 declare to be sustainable, but there’s still room for improvement
- Almost half of the companies have the expertise and skills for implementing transformation 4.0. The other half focus on training and the market
- For the first time, MECSPE will be at BolognaFiere from 23 to 25 November 2021 to showcase supply chain excellence, boost the manufacturing sector and connect companies with young talents.
Milan, 27 July 2021 – the wind of economic recovery is blowing across Italy. Positive signals are arriving from the European Commission (the Italian GDP is growing by 5% in 2021), as the trend of Italy’s real economy confirms. Things are changing even for the manufacturing sector – the backbone of Italy’s economic fabric – which is looking at the future with more confidence. According to Senaf’s latest MECSPE Observatory (BolognaFiere, 23-25 November 2021), in the second quarter[1], seven companies out of ten (69%) are expecting an increase in turnover at the end of 2021. It could be an easy guess, given the difficulties of 2020. But in February, less than half of the entrepreneurs believed in this growth. Their order portfolio, which reached satisfying levels (according to 72% of the respondents), and the market forecast confirm this wave of optimism. 74% of respondents believe that the sector will boom again within the next 3 years. Even companies’ confidence is improving (it’s high for 54% of them compared to 39% in February). What are the major trends at the moment? Digitisation, sustainability, and training are the driving forces of the manufacturing sector’s cultural change. They will be the hot topic at the first MECSPE edition in Bologna.
Digitisation: what have we learned from the pandemic, and what is the future holding, given the NRRP and ISW?
One of the biggest lessons we’ve learned from the pandemic is that there’s no future without digital growth. Entrepreneurs know this well, especially the 27% of them who invested in digitisation after the Covid-19 outbreak. So what does digitisation mean for the manufacturing sector? Investments in 2021 must focus on state-of-the-art technologies and processes, such as cybersecurity, 5G connection, Internet of Things, collaborative robotics. It also means seizing the opportunities provided by new regulations such as the National Recovery and Resilience Plan (NRRP), approved a few weeks ago.
Despite its wide media coverage, only one entrepreneur out of ten (15%) knows the content of this plan. This aspect is crucial given all the measures contained in the NRRP that can make a difference for the manufacturing sector.
One of these measures is the allocation of € 350 million, in 2021-2026, for Competence Centres and Digital Innovation Hubs to drive companies towards the 4th industrial revolution. So far, only 8% of companies have collaborated with one of these centres/hubs. 46% of them don’t even know about their existence. However, more than one-third of respondents believe that Competence Centres will support companies in building and testing Industry 4.0 projects, and Digital Innovation Hubs will raise awareness on Industry 4.0 opportunities. But the road ahead is still long. Therefore, we need to accelerate the cultural change by informing the supply chain players so that they can attract young people to the smart factory world. This year, MECSPE has introduced the Piazza Competence Centre to put visitors in contact with the eight Competence Centres so that they can learn about their innovative training and orientation projects within industry 4.0. Digitisation and smart factory will also be at the centre of Gamification: the limitless factory. This session will show the best technological ideas that drive the most innovative solutions. The aim is to promote a new human-scale factory that can attract young talents.
The transformation of the past year and a half has led us to reflect on Industrial Smart Working (ISW). This work method allows us to manage and carry out production processes remotely. Only 15% percent of entrepreneurs doesn’t consider ISW suitable for the industrial sector, believing that on-site presence is the only option possible. Perhaps, the latest events can dismantle this belief so that a cultural change can begin.
Over one-third of the respondents believes that ISW is helpful only if combined with on-site presence. Others think ISW is interesting, but industrial resources and processes/tools must be reorganised to be effective.
The perceived benefits include greater flexibility for employees (41%) and cost reduction (29%).
Sustainability: going green to attract investments and improve reputation
Going green is no longer an option but a social obligation. Today, 40% of companies have adopted a sustainable approach. They use low-power devices, efficient, state-of-the-art machines and/or systems, and electrical and thermal energy from renewable sources.
ESG (Social, Environmental, Governance) criteria define companies’ virtuous behaviours. These parameters help assess the impact of a business and play a major role in attracting investments and improving a company’s reputation. However, only one company out of three (32%) knows these parameters, with larger companies paying more attention to them. How? For example, following good practices and ethical principles (42%) and introducing measures to improve employees’ wellbeing and work quality (24%). MECSPE will also promote ESG and sustainability through two special events: ECOfriendly initiative – “Io faccio di più”, a virtual and real journey for exhibitors who adopt environmentally-friendly policies as part of their company strategies and production processes. The other event is the Materioteca Design Area dedicated to “Blue economy”, which takes sustainability to the next level, creating value from waste through scientific and creative solutions.
Training: focusing on human capital for the future of the manufacturing sector
Continuous technological innovations pose a serious question: do companies have all the competencies needed to complete transformation 4.0? 46% of the respondents answered positively, pointing out that they have already trained their personnel and will hold refresher courses. One company out of ten (10%) preferred hiring already trained personnel. Other companies (17%) are planning to hire personnel with relevant skills. However, 27% of the respondents admitted that they are not ready yet. With these preconditions, training becomes crucial for maintaining competitiveness, and universities and technical institutes will play a crucial role. MECSPE’s mission is to connect companies with young talents to relaunch Italy’s manufacturing sector. Years ago, this trade fair started a collaboration with the CNOS-FAP Federation. Moreover, every edition gives a lot of space to training and refresher workshops and hands-on demonstrations to attract youngsters to the Industry 4.0 world.
MECSPE by the numbers (as per 15 July 2021)
An exhibition surface of 92,000 sq.m, 1,800 attending companies, 2,000 sq.m dedicated to the Limitless Factory Exhibition Core, 46 special events and conferences. 50,000 professional visitors are expected to attend the event in full safety.
MECSPE Halls
Tools and machines – Machine tools, Equipment, Tools, Design software; Machinery, materials and sheet metal working – Bending, Moulding, Cutting, Assembly, Welding, Materials and Software; Digital Factory – Industrial computing, IoT, Industrial sensors, Cloud-manufacturing, Automatic identification technologies, Applications, devices, instrumentation, and smart components for interpreting and interconnecting processes; Logistics – Wrapping, Packaging, Handling, Material handling, Lean manufacturing, Warehouse management software, Supply chain management, Safety systems, PPE, Outsourcing; Mechanical subcontracting – Precision mechanical processing, Metal carpentry, Mechanical construction, Fasteners, Foundries, Small parts, Wire working, Outsourced industrial processes, Micro-processing; Electronic subcontracting – CEM (Contract Electronics Manufacturer), Wiring, EMS (Electronics Manufacturing Service), PCB (Printed Circuit Board Manufacturers), Engineering and design firms; Moulds, Machines and plastic, rubber and composite subcontracting – Plastics, rubber, and composite processing, Machines and plants, Auxiliary equipment, innovative materials, Moulding, Extrusion, Packaging, Blow Moulding, Moulds, Models, Normalised parts for moulds, Design, Simulation and design software, Micro-processing; Additive Manufacturing – 3D printing, Rapid prototyping, Rapid manufacturing, Systems and services for reverse engineering, Additive technology, Materials, Services, Hardware: 3D printers and scanners, accessories, Simulation and design software; Treatments and Finishes – Surface treatment systems, Furnaces, Galvanic finishes, Chemical and electronic processes, Washing, Metallising, Glazing, Galvanising, Products and accessories for treatments, Thermal treatments, Painting; Non-ferrous materials and alloys – Processing of non-ferrous materials (Aluminium, Titanium, Magnesium, Light Alloys), Die-casting, Foundries, Outsourced industrial processes, Technologies, Design, Engineering; Automation and Robotics – Automation and Robotics, Assembly, Mounting and handling; Quality and Control – Quality certification and control, Metrology, Measurement instruments, Laboratory tests, Calibration, Analysis equipment, Vision systems; Power Drive – Mechanical power transmission systems, Hydraulics, Pneumatics, Mechatronics, Motion control, Maintenance, Compressed air.
For information, www.mecspe.com
For further information
Press office
MY PR – www.mypr.it
Roberto Grattagliano – Fabio Micali
mobile ph._ 338 9291793 tel_ 340-8758736
e-mail roberto.grattagliano@mypr.it – fabio.micali@mypr.it
[1] Methodological note: The MECSPE Observatory was conducted by GRS Research and Strategy on a sample of 619 Italian companies in the mechanical sector using the CAWI (Computer Assisted Web Interviewing) method.